Torsion Tower Structure
The robot can work in any environment without demanding high airtightness or a smooth surface.
The robot can function efficiently for a long time without collapsing because the torsion tower structure does not depend on the material's elasticity and recovery properties.
Conceptual Design
The crease design references two formulas that relate different variables together. After thorough calculations and estimations, we designed a crease to be folded and manufactured into a torsion tower structure. The figures below demonstrate a detailed process of how we initiated the idea of designing torsion tower structures, finalized the formula and stretch references after conducting literature reviews, confirmed the numbers in the design like the length, width, height, and angle of the torsion tower structure, and created a two-dimensional drawing with AutoCAD.



Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-3 are referenced from researches conducted by professors at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign on a crawling robot driven by multi-stable origami (Pagano et al., 2017).
Pagano, A., Yan, T., Chien, B., Wissa, A., & Tawfick, S. (2017). A crawling robot driven by multi-stable origami. Smart Materials and Structures, 26(9), 094007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665x/aa721e
Detailed Design

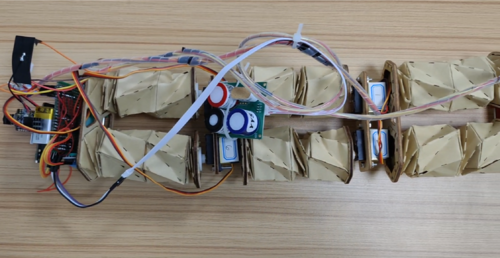
We made two generations of the crease design. The first generation involves dividing the torsion tower structure into six rows and four layers and adding margins on the side for connection purposes. After experimenting with the first design, we learned that the horizontal creases might collapse inward when encountering resilience, causing the torsion tower structure to malfunction. The second generation has one more horizontal crease composed of three edges, increasing the strength of the horizontal creases and the robot's lifespan. The robot’s extended lifespan can better the innovation’s reputation in the community of farmers, environmental organizations, and governments as a reliable and sustainable robot, increasing the chance of positive feedback and potentially boosting the number of consumers and trading volumes.

When the torsion tower structure is damaged because of conditions like collapsing or over-twistings, the modularization of the robot allows consumers to buy and substitute only the torsion tower structure but not other parts of the robot at a low cost. The modular substitution nature of the robot also emphasizes reusing under the framework of environmentalism as it allows the robot to be repaired by only purchasing the torsion tower structure and avoids the need to consume and produce other components of the robot.

Compared to those made from polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene, polyimide film, and printing paper, the torsion tower structure made from kraft paper is the best because it is easy to fold and twist, does not collapse easily, and has hard edges and corners after folding. The three characteristics can extend the robot’s lifespan and avoid the need to purchase the robot again in a short period.

